iSAS
Innovate for Sustainable Accelerating Systems

Innovate for Sustainable Accelerating Systems
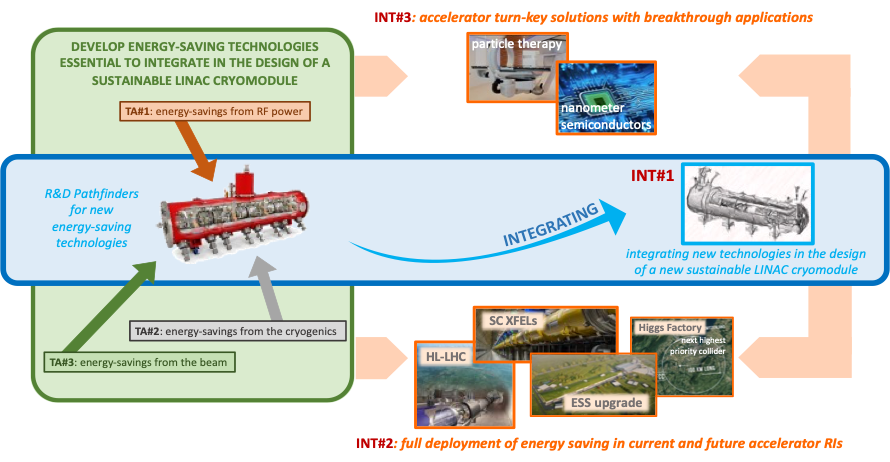
Directly connected to the superconducting RF accelerating system itself, three key Technology Areas (TAs) where power is lost have been identified. The objective of iSAS is to develop, prototype and validate new impactful energy-saving technologies so that SRF accelerators can operate with the same or improved performance while using significantly less energy. Leveraging, and complementary to, current technological advances, the most promising and impactful technologies will be developed to increase their Technology Readiness Level (TRL) with a view to enabling industry to fabricate new tools for integration into the largest European RIs such as HL-LHC, ESS and EuXFEL and/or in the design of future accelerator-driven RIs. Towards the end of the project, an important objective is to organize a peer review to quantify and assess the achieved energy-saving performances of the iSAS technologies and to disseminate the report.
TA#1: energy-savings from RF power – While great strides are being made in the energy efficiency of various RF power generators, the objective of iSAS is to ensure additional impactful energy savings through coherent integration of the RF power source with smart digital control systems and with novel tuners that compensate rapidly cavity detuning from mechanical vibrations, resulting in a further reduction of power demands by up to a factor of 3.
TA#2: energy-savings from cryogenics – While major progress is being made in reusing the heat produced in cryogenics systems, the objective of iSAS is to develop superconducting cavities that operate with high performance at 4.2 K (i.e., up to 4.5 K depending on the cryogenic overpressure) instead of 2 K, thereby reducing the grid-power to operate the cryogenic system by a factor of 3 and requiring less capital investment to build the cryogenic plant.
TA#3: energy-savings from the beam – Significant progress has been achieved in maintaining the brightness of recirculating beams to provide high-intensity collisions to experiments, but most of the particles lose their power through radiation or in the beam dump system. The objective of iSAS is to develop dedicated power couplers for damping the so-called Higher-Order Modes (HOMs) excited by the passage of high-current beams in the super-conducting cavities, enabling efficient recovery of the energy of recirculating beams back into the cavities before it is dumped, resulting in energy reduction for operating, high-energy, high-intensity accelerators by a factor ten.
Through developments at leading European laboratories acting as R&D Pathfinders, significant energy savings are within reach for each of the above technologies when integrated into accelerator facilities and industrial applications. Enabled by the unique iSAS collaboration and the joint investment between research institutions and industry, iSAS envisages three Integration Activities (INTs) to introduce energy-saving technologies into research facilities.
INT#1: integration into the design of a sustainable LINAC cryomodule – While LINAC cryomodules are designed for specific accelerators, the objective of iSAS is to address the common engineering challenges of integrating iSAS technologies into a parametric design of a new sustainable accelerator system.
INT#2: integration into existing RIs – While various RIs envisage upgrades, the objective of iSAS is to expedite the technical integration of energy-saving technologies by retrofitting existing accelerating systems. A cryomodule will be adapted, ready to demonstrate energy recovery of high-power recirculating beams in the PERLE research facility, paving the way for high-energy, high-intensity electron beams with minimal energy consumption.
INT#3: integration into industrial solutions – While iSAS technologies are emerging, the objective of iSAS is to plan for concrete co-developments with industry to expedite reaching a TRL sufficiently advanced towards large-scale deployment of the new energy-saving solutions at current and future RIs as well as to prepare the path for industrial applications. For many future RIs and industrial applications SRF is the enabling technology.
The long-term ambition of iSAS is to catalyse the implementation of the European Accelerator R&D Roadmap. Accordingly, the objective of iSAS is not only to prepare the technology readiness to achieve impactful energy savings at RIs, but also to train experts and newcomers in the field. They will be trained to leverage the iSAS project by further developing sustainable accelerating technologies and eventually to operate them when integrated in RIs and in industrial applications. iSAS will contribute to the acceptance of sustainable accelerators in a green Europe.